Freewheels are machine elements with particular characteristics:
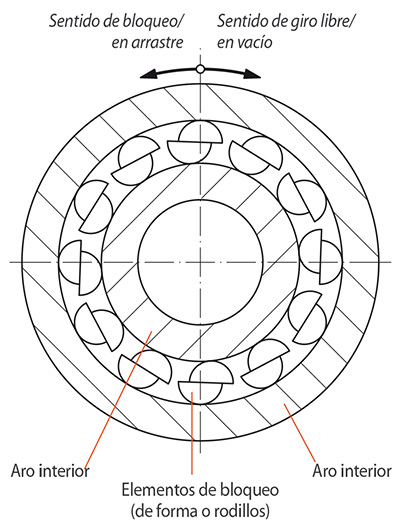
- In one direction of rotation there is no contact between the inner and outer ring; the freewheel is in freewheeling operation.
- In the other direction of rotation there is contact between the inner and outer ring; in this direction it is possible to transmit high torque.
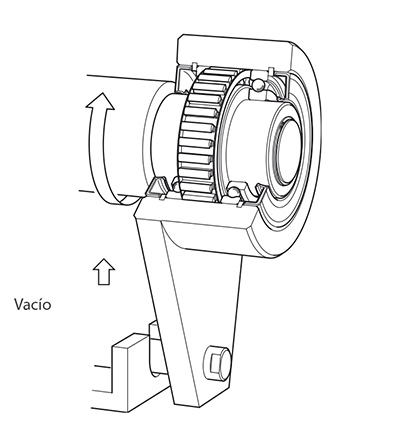
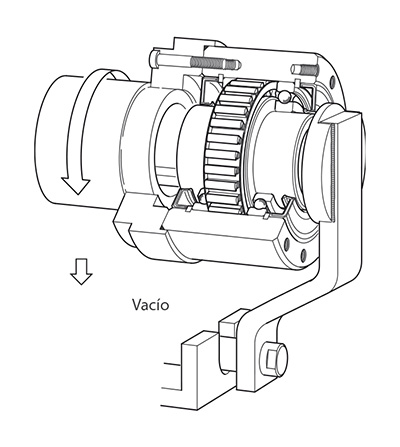
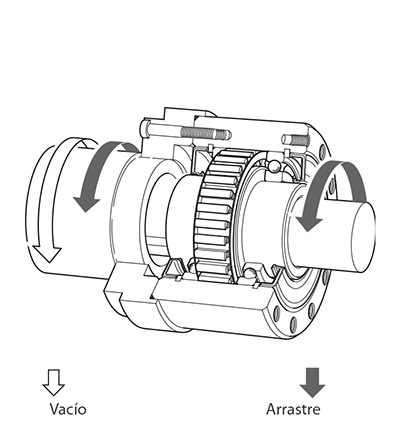
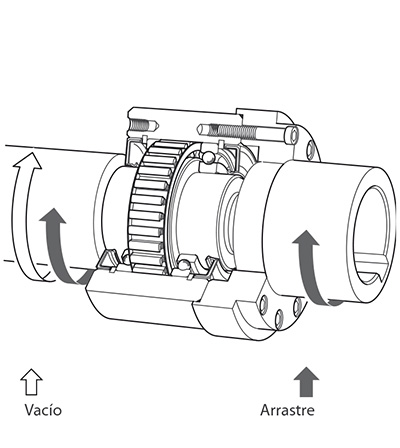
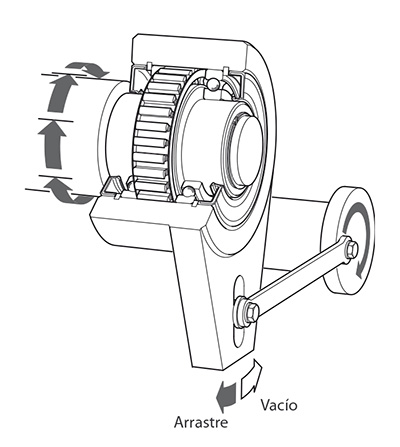
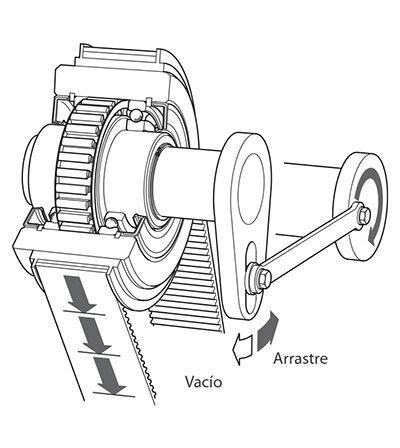
For example the outer ring of the freewheel shown in the figure beside can freewheel clockwise while the inner ring is stationary. If, however, the outer ring is turned in the opposite direction, there is contact between the inner and outer ring and the inner ring is driven (driving operation).
Freewheels are used as:
- Backstops
- Overrunning Clutches
- Indexing Freewheels
Freewheels can fulfill these functions completely automatically in the most diverse machines. No mechanical or hydraulic operating equipment is required, as for example with external actuated clutches or brakes.
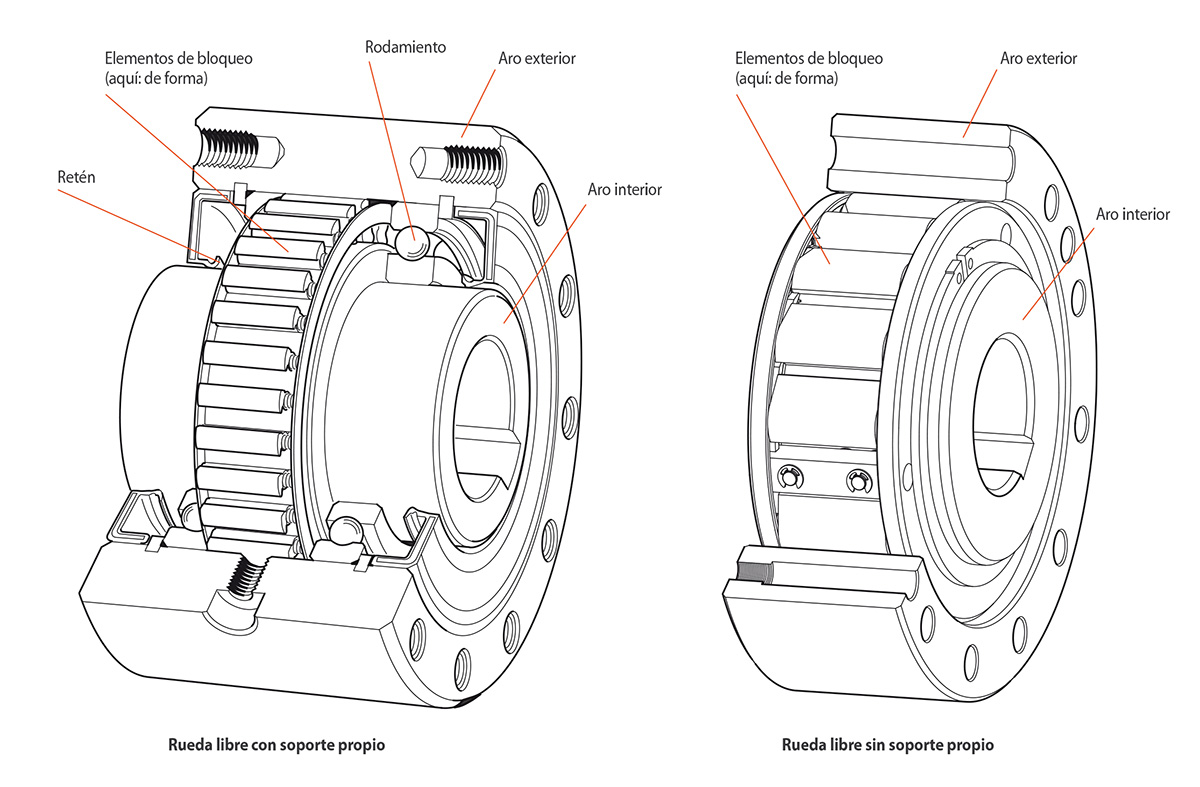
Freewheels consist of an inner and an outer ring between which clamping elements are arranged. Clamping elements can be sprags or rollers. We differentiate as follows:
- Freewheels with bearing support and
- Freewheels without bearing support.
For a freewheel to function, the concentric alignment of the inner and outer ring is required. In the case of freewheels without bearing support, concentric alignment like this must be provided by the customer.
RINGSPANN freewheels are an indispensable design element in the machine building industry as well as in the aerospace industry. Many designs are only economical if freewheels are used. The freewheel as an automatic driving element is preferred to conventional solutions because it offers the following significant
advantages:
- operating safety,
- efficiency and
- a higher degree of automation.
With more than 50 years experience in the development, production and sales of freewheels, RINGSPANN offers the most comprehensive range of freewheels. A global network of subsidiaries and sales agencies ensures the best possible personal on-site service. Assembly and production facilities in various countries provide fast, reliable delivery.